Kubernetes Overview
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Key points include:
- Developed originally by Google, now maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation
- Designed to run distributed systems resiliently
- Provides features like service discovery, load balancing, storage orchestration, and self-healing
- Enables declarative configuration and automation
Kubernetes Architecture
Kubernetes uses a master-worker architecture:
-
Master Node (Control Plane):
- API Server: Central management point for the cluster (this is the frontend for the cluster)
- Scheduler: Assigns work to nodes
- Controller Manager: Regulates the state of the system
- Cloud Controller Manager: Regulates the state of the system, in case we are using a cloud provider
- etcd: Distributed key-value store for cluster data (mini database)
-
Worker Nodes:
- Kubelet: Ensures containers are running in a pod
- Container Runtime: Software for running containers (e.g., Docker)
- Kube-proxy: Manages network rules on nodes
Other architectures
Orchestrated architecture
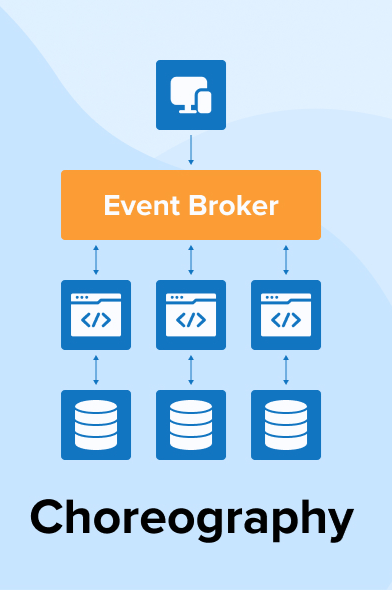
Key Kubernetes Concepts
-
Clusters:
- A set of nodes that run containerized applications
- Provides high availability and scalability (you can have replicas in different datacenters)
-
Nodes:
- Physical or virtual machines in the Kubernetes cluster
- Can be master nodes (part of the control plane) or worker nodes
-
Namespaces:
- Virtual clusters within a physical cluster
- Used for organizing resources and multi-tenancy
-
Pods:
- Smallest deployable units in Kubernetes
- Can contain one or more containers
- Share network namespace and storage
-
- Describe the desired state for a set of pods
- Provide basic scaling and self-healing mechanisms
-
- An abstract way to expose applications running on pods
- Provide a stable network endpoint
-
Persistent Volumes (and Persistent Volume Claims):
- Abstraction for storage resources in the cluster
-
- Manage configuration data and sensitive information
-
- Manage external access to services in a cluster
